A lot of people including few or more of healthcare professional don’t know how antibiotic resistance is developed or they don’t recognize the real risk of their contribution in antibiotic resistance either by overusing certain classes of antimicrobial all the time which is known as “Selective pressure” or abusing antibiotics when there is no real need for prescribing antibiotics.
For example, a surgeon in a well established healthcare facility in X country, he always concerned about patients coming with intra-abdominal infections. The management process of such infections requires antimicrobial therapy. The IDSA guidelines recommends a set of antibiotics that can be used for the treatment and to achieve complete microbiological eradication. The surgeon is allowed to use piperacillin/tazobactam without infectious disease revision and the result is? every single patient coming with intra-abdominal collections is treated with piperacillin/tazobactam unless the treatment failed for a reason or another or culture data released showing that the patient infection is resistance to piperacillin/tazobactam and an ID consultation is required putting the patient at risk of mortality and morbidity as well as longer hospital stays and for sure extra costs.
The previous example is a very common scenario that is being repeated with different classes of antibiotics and recently you must have read about a resistance strains of bacteria to almost every known antibiotics (PAN resistance) :
http://www.bbc.com/news/health-38609553
https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/66/wr/pdfs/mm6601a7.pdf
It is very important to read CDC report, they try to be optimistic and we have to but with caution, they reported the following:
CRE “carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae” is common and they are reported to CDC as a part of surveillance programs and the resistance to all known antibiotics is uncommon however, this is an alarming note that resistance is emerging and there is a reported cases like the one mentioned above resistance to all known antibiotics.
Infection control and proper applied antimicrobial stewardship programs are key factors in fighting anti-microbial resistance. I have seen many hospitals with stewardship program on papers only!
Lets move to the reasons of Antimicrobial Resistance:
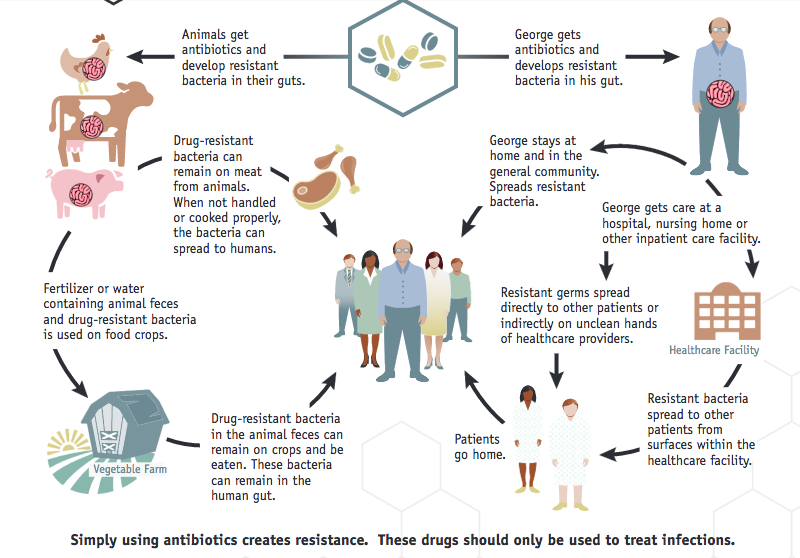
- Once you ingest an antibiotic for an infection, the antibiotic has its effect on both good and harmful bacterial. However, some strains of bacteria doesn’t affected by such antibiotic for many reasons like the antibiotic has no coverage for such strains or they already developed a resistance to that antibiotic.
- Now the antibiotic works and the infection is treated but the non susceptible strains may have identified the antibiotic and developed a technique to fight its action ( e.g efflux for tetracyclines) so they become resistance.
- These resistance strains may transfer the genes responsible for the resistance to another different strains and resistance emerges with more and more strains.
So, to avoid antibiotic resistance it is crucial for every healthcare professional who allowed to prescribe antibiotics to NOT prescribe unless there is a real need and to monitor the local antibiogram data to get a general idea how antibiotics work in the treatment settings, and what are the resistance patterns to different classes of antibiotics.