To find part 1 please click here.
We talked about how important the calcium for your bones , other things you need to know about calcium supplementation :
- Calcium dietary supplements can interact or interfere with certain medications or drugs you take & some medication may increase or decrease calcium level in your blood.
- Calcium is the most important in group aged from 9-18 years , this is the time for building the bone density.
- Bone density starts to decline after the age of 35 years old.
As the decrease in density is very slow and silent you will never know if you didn’t check your bone density regularly!
The lower bone density the :
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a progressive disease that causes the bones to become porous and fragile and then more susceptible to fractures.
The most susceptible parts in your body to fractures :
- Spine.
- Hip.
- Wrist.
As it is silent disease ( Usually no symptoms until you fracture a bone ) , 1 in 3 women and 1 in 5 men will get this disease.
When you can’t get enough calcium , your bone’s calcium reabsorbed by the body leaving your bones fragile! Calcium and phosphate are the two minerals essential for bone formation , in youth your body uses these minerals to form bones , as you age plus you don’t take enough calcium , these minerals again my be reabsorbed leaving your bones weak and more prone to fracture even without injury!
So to summarize the causes and risk factors of Osteoporosis :
- In women the drop in estrogen at menopause and in men the drop of testosterone.
- Women over age of 50 and men over age of 70 have a higher risk for Osteoporosis.
- Chronic rheumatoid arthritis , kidney disease or eating disorder.
- Taking corticosteroid medications.
- Hyperparathyrodism (Long word :biggrin: )
- Low vitamin D intake ( no utilization of calcium in the bones)
- Family history of Osteoporosis .
Symptoms ?
There is no symptoms in the early stages of the disease we called it silent disease :face:
Symptoms occur in the late stage include :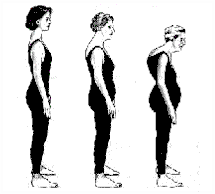
- Bone pain and tenderness
- Fractures.
- loss of height ( curved body shape )
- low back pain.
- Neck pain.
- Stooped posture or kyphosis ” dowager’s jump “
How to test Osteoporosis :
There are many test to diagnose Osteoporosis :
- Bone mineral density testing using densitometry or DEXA scan.
- Special type of spine CT that can show loss of bone mineral density.
- Quantitative computed tomography (QCT) may be used in rare cases.
- In severe case spine or hip X-ray may show fracture or collapse of the spinal bones however X-ray is not very accurate in detecting whether someone has Osteoporosis or not.
- Blood and urine tests may be needed if you develop Osteoporosis due to other related medical problem rather than older age.
Managing and treatment of Osteoporosis :
The goals in treating osteoporosis are to control the pain from the disease and slow down or stop the bone loss and giving medications to strengthen the bones to prevent fractures , also minimizing the risk of falls that may lead to fractures.
A . Medications :
The goal of using medication is to strengthen the bones when :
- Osteoporosis has been diagnosed by bone density study.
- Osteopenia , the bones become thin.
- Fracture has occurred.
Types of medications :
- Biphosphonates : Primary drugs used to both prevent and treat Osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. They include Alendronate , ibandronate & risedronate. Usually taken by mouth once a week or once a month.
- Hormone Therapy : Estrogen or hormone replacement therapy ( HRT ) is rarely used anymore to prevent Osteoporosis and are not approved to treat a woman who has already been diagnosed with the disease conditions.
- Raloxifene : is used for prevention and treatment of Osteoporosis , it reduces the risk of spinal fractures by almost 50% However, it doesn’t appear to prevent other fractures including fractures in hip, it may have protective effect against heart disease and breast cancer through more studies are needed.
B. Life Style Modification :
1. Exercise , regular exercise can reduce the likelihood of bone fractures in people with Osteoporosis. Some of the recommended exercises include :
- Weight bearing exercises , walking , jogging or playing tennis.
- Resistance exercises , free weights , weights machines & stretch bands.
- Balance exercises , tai chi & yoga.
- Riding a stationary bicycle.
- Using rowing machines.
Try to avoid any exercise that has a risk of fall or high impact exercises that may cause fractures.
2. Diet : Get at least 1200 mg per day of calcium , you can re-vise the recommended allowance per day through this link , and 800 -1000 IU of Vitamin D.
Following a diet that provide a proper amount of calcium , vitamin D and protein , while this will not completely stop the calcium loss from your bones but it will guarantee that a supply of the materials the body uses to from and maintain the bones are available.
High Calcium food include : Cheese , Ice cream :biggrin: , leafy green vegetables (like spinach and collard greens ), salmon ,sardines ,Yogurt ..etc
Life style modification also include stopping unhealthy habits like stop smoking , alcohol intake as too much alcohol damage your bones.
for people who have Osteopenia or risk of Osteoporosis , they should be cautious about falling risk !
Preventing falls :
- Avoid sedating medications and remove household hazards to reduce the risk of fractures.
- Be sure your vision is good.
- Always watch your steps.
- Avoid walking alone on icy days.
- Use bars in bath hubs when needed.
- Wear well-fitting closes and shoes.
